Roofing Terms
Glossary of roofing terms
ASTM The American Society for Testing and Materials; organization that sets standards for a wide variety of materials, including roofing.
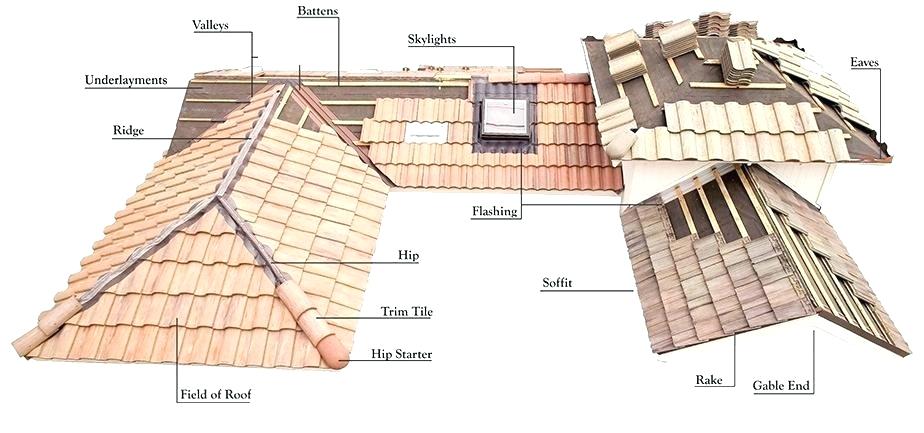
BARGE BOARD A board that conceals roof timbers projecting over gables.
COUNTER FLASHING That portion of the flashing attached to a vertical surface to prevent water from migrating behind the step flashing.
CORNICE The overhanging part of the roof (the part that sticks out past the walls).
CRICKET The evaluation of a part of a roof surface as a means of promoting drainage of water from behind an obstacle such as the chimney.
CURB A short wall or masonry built above the level of the roof; it provides a means of flashing the deck equipment.
DECK The base surface to which a roof system is applied.
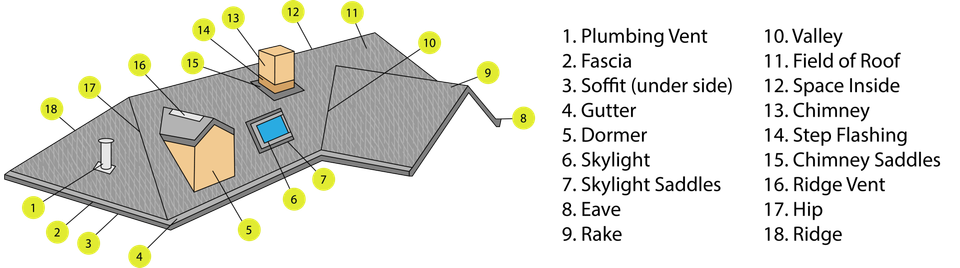
DORMER A structural element of a building that protrudes from the plane of a sloping roof surface; creates a usable space in the roof of a building by adding headroom and usually also by enabling the addition of windows.
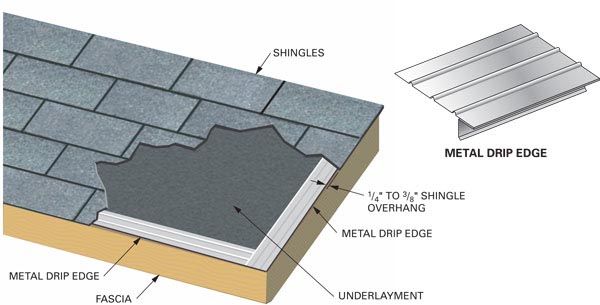
DRIP EDGE A device designed to prevent water from running back or under an overhang.
EDGE METAL A term relating to brake or extruded metal around the perimeter of a roof.
EAVE The part of a roof which projects out from the side wall, or the lower edge of the part of a roof that overhangs a wall.
FASCIA Any cover board at the edge or eaves of a flat, sloping, or overhanging roof, which is placed in a vertical position to protect the edge of the roof assembly.
FELT A very general term used to describe composition of roofing ply sheets, consisting of a mat of organic or inorganic fibers unsaturated, impregnated with asphalt or coal tar pitch, or impregnated and coated with asphalt.
FLASHING Connecting devices that seal membrane joints at expansion joints, walls, drains, gravel stops, and other places where the membrane is interrupted or terminated.
GABLE Triangular roof (the part of a wall that encloses the end of a pitched roof).
GUTTER A narrow channel, or trough, forming the component of a roof system, which collects and diverts rainwater shed by the roof.
HIP ROOF A roof which rises by inclining planes from all four sides of a building.
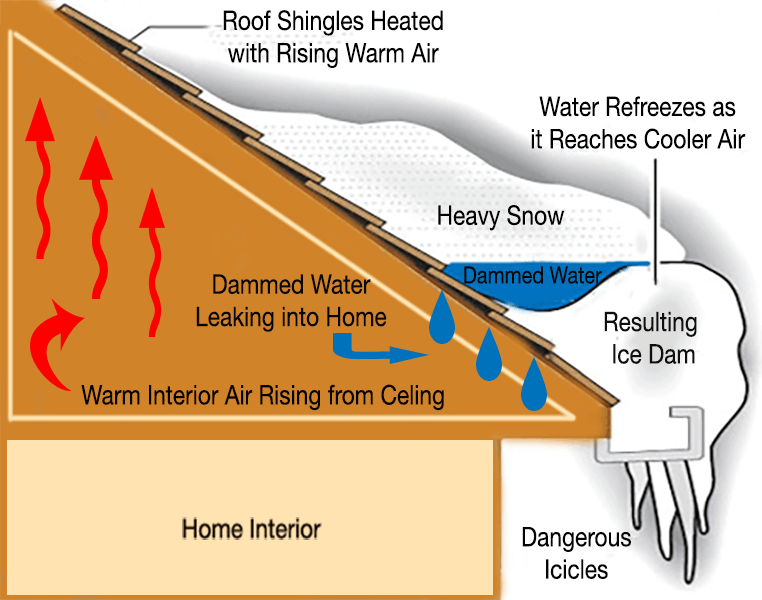
ICE DAM Condition formed at the lower roof edge by the thawing and re-freezing of melted snow on the overhang. Can force water up and under shingles, causing leaks.
OSB Oriented Strand Board A decking made from wood chips and lamination glues.
PLUMBING VENT (SOIL PIPE VENT) Consists of pipes leading from fixtures to the outdoors, usually via the roof. Vents provide for relief of sewer gases, admission of oxygen for aerobic sewage digestion, and maintenance of the trap water seals which prevent sewer gases from entering the home.
PLYWOOD Thin layers of boards that are glued, compressed and laminated to create a thicker board; thin layers of wood placed together with the grain of each layer at right angles to the adjacent layer.
RAFTER Parallel beams that support a roof (similar to how joists support floors and ceilings).
RAKE The angle of slope of a roof rafter, or the inclined portion of a cornice.
RIDGE The uppermost, horizontal external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes.
RIDGE VENT A ridge vent runs the entire length of the roof peak, blending into the roofline for a more attractive home.
RIDGE CAP Shingles used to cover the horizontal external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes.
ROOF DECK A component in building construction, which forms a platform on which the remainder of the roof components are placed.
SHEETING The boards of sheet type material, plywood or asphalt saturated sheets, nailed to studding or roofing rafters as the base for application of the roof covering.
SKYLIGHT A flat or sloped window built into a roof structure for daylighting.
SLOPE Incline or pitch of roof surface.
SOFFIT The underside of a part or member of a building extending out from the plane of the building walls.
SOFFIT VENTILATION Intake ventilation installed under the eaves, or at the roof edge.
SQUARE A term used by the roof industry to indicate an amount of roof area equal to 100 square feet.
STEP FLASHING Flashing application method used where a vertical surface meets a sloping roof plane.
TEAR OFF A term used to describe the complete removal of the existing roofing system down to the sheeting.
TRUSS A framework of beams (like ribs) that support the roof (usually triangular).
VALLEY A depressed angle formed by the meeting of two inclined slopes of a roof.
VENTING A process of installing roof vents in a roof assembly to relieve vapor pressure; types of ventilation include ridge (attic), soffit, and plumbing